Data Deduplication can save valuable amounts of hard drive space. In today’s cost conscious environments, saving hard drive space can translate into budgets that can be utilized elsewhere. The question that often pops up is “How much space will data dedup save me?” Unfortunately, there is no way to make a accurate prediction. Data dedup works best with static data. That is because there is no reason to dedup data that changes often.
The PowerShell code below will generate a few thousand text files that will share a lot of common bit patterns. This will help to demonstrate some space savings with dedup.
And now to see what we got back:
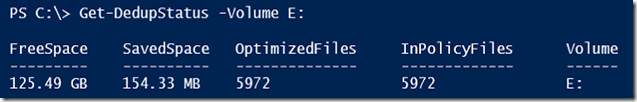
This may not seem like a lot of savings for 10,000 files, but then again these were small files for the most part. You results will vary. In the end, this could be used as a tactic to free up space on hard drives that are critically short on space. Also take a look at the File Server Resource Manager for more tools to help identify data that may be able to be moved to offline storage.
The PowerShell code below will generate a few thousand text files that will share a lot of common bit patterns. This will help to demonstrate some space savings with dedup.
$String
$NewLineIndex = 0
For ($X=0;$X -lt 10000;$X++)
{
$C1 = [Char]((Get-Random(35)) + 65)
$C2 = [Char]((Get-Random(35)) + 65)
$C3 = [Char]((Get-Random(35)) + 65)
$C4 = [Char]((Get-Random(35)) + 65)
$String += "$($C1)$($C2)$($C3)$($C4) "
If ($NewLineIndex -gt 15)
{
$Strgin += "`n"
$NewLineIndex = 0
}
$Name = "E:\PS\Files$($X).txt"
$NewLineIndex++
$String | Out-File -LiteralPath $Name
}
Executing this code will generate a lot of files, but this will also help make more of a visual impact with this demonstration. Once this code has executed, we need to install the data deduplcation
Install-WIndowsFeature FS-Data-Deduplication
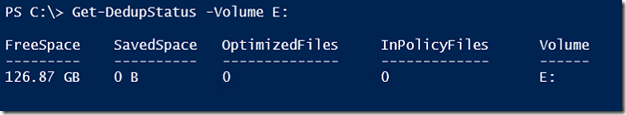
Once this feature is installed, you need to enable this feature on the volume that is holding your data. In this case, it is the E: drive.
Enable-DedupVolume –Volume E:
Data deduplication will only work when scheduled and on data that is at least 5 days old. To make this demo work, we need to set the age requirment to 0 days.
Set-DedupVolume –Volume E: –MinimumFileAgeDays 0
Now we can start a deduplication. To see our space savings:
Get-DedupStatus –Volume E:
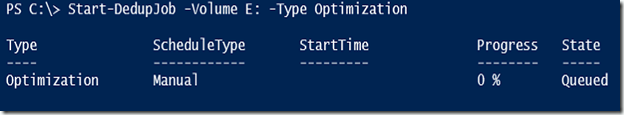
Now we can start the deduplication.
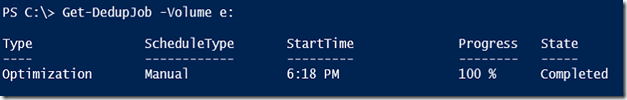
You can check the status of the deduplication job:

This may not seem like a lot of savings for 10,000 files, but then again these were small files for the most part. You results will vary. In the end, this could be used as a tactic to free up space on hard drives that are critically short on space. Also take a look at the File Server Resource Manager for more tools to help identify data that may be able to be moved to offline storage.
Comments