Configuring resource reserves for a Host in VMM is a good idea. This prevents the VMs running on the host from consuming all the resources of that host and rendering it unusable. There are two ways of setting up host reserves, manually and through inheritance.
Let’s first look at the inheritance method. Below is a screen shot of my VMM host groups.
Currently, I have the default host reserves set on them. The image below is from the All Hosts properties.
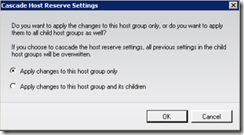
I’m going to change the CPU percentage from 20 to 25 and then click OK. When I did this, I received the options below.
I’m going to select Apply changes to this host group and its children and click OK
Once completed, the host reserves for the host currently on that host group did not change. This is for new hosts added to VMM. This is not the true inheritance that we use with technologies such as NTFS. The Host Reserves in the Host Groups should be considered more as templates for new hosts as opposed to an inheritable property
The Manual method is how you change the host reserves for VMM hosts that are already managed by the VMM server. You simply right click the host and select Properties. Then click the Reserves tab and make your changes.

Comments