The question from class was how to set a mailbox to autoreply to the sender. In this case, if the sender is requesting support, this auto response will let them know that their email has been received. It turns out this is a simple one liner in PowerShell.
The below command is one continuous line. This needs to be execute in the Exchange Management Console on the Exchange server.
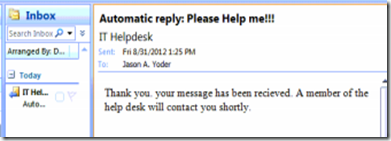
Below is how it appears in Outlook for the user who sent the request.
If you expect email from outside your organization, you can also set an external rule.
The below command is one continuous line. This needs to be execute in the Exchange Management Console on the Exchange server.
Set-MailboxAutoReplyConfiguration –Identity ITHelpdesk –InternalMessage “Thank you. Your message has been received. A member of the help desk will contact you shortly.” –AutoReplyState Enabled
Below is how it appears in Outlook for the user who sent the request.

If you expect email from outside your organization, you can also set an external rule.
Set-MailboxAutoReplyConfiguration –Identity ITHelpdesk –InternalMessage “Thank you. Your message has been received. A member of the help desk will contact you shortly.” –ExternalMessage “Thank you. Your message has been received. A member of the help desk will contact you shortly.” –AutoReplyState Enabled
Comments