Windows Thin Client allows you to take legacy hardware and continue to utilize it using modern operating systems. This is done through the usage of Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2008 R2.
When booting the ISO file for Windows Thin Client, you will get the usual imagery.
Select the language of your choice and click Next
Click Install Now
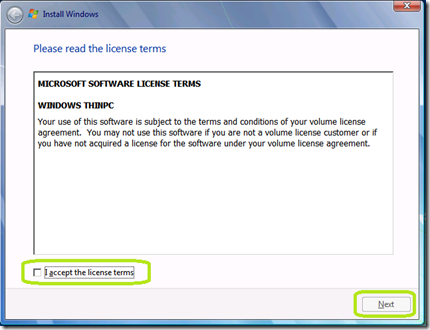
Check I accept the license terms and click Next
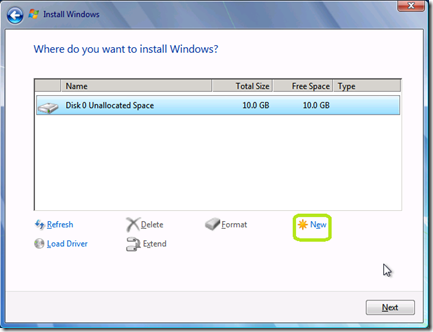
Select the drive that you want to install Windows Thin Client on.
If this is an unformatted drive, click Drive options (advanced).
Click New
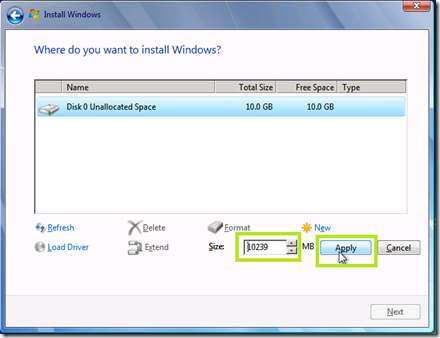
Determine how much of the hard drive that you want to format and click Apply.
Click OK at the message below.
Click Next
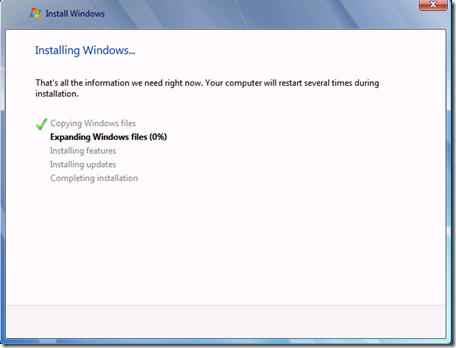
The installation will now run.
Provide a name for the first account on this system and a name for this PC. Remember, this is a local administrator for this client.
Provide and confirm a password for this account. Also provide a hint for this password. Click Next when completed.
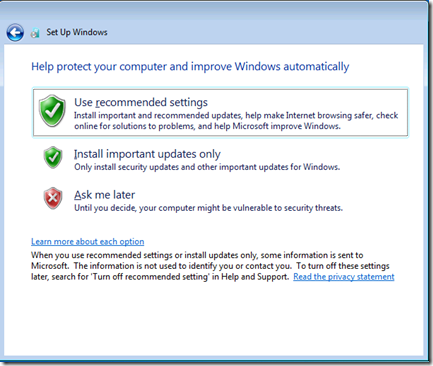
Select the update policy that is appropriate for your environment.
Select to appropriate time and date settings.
Configure the appropriate firewall policy for the connection this thin client is on.
Let Setup complete.
The thin client is now installed.
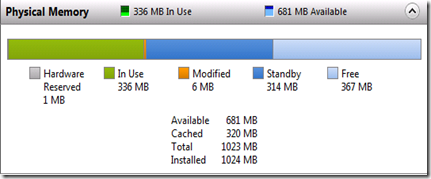
This installation of Windows Thin Client consumed only 2.98 GB. Below is a snap shot of the thin clients memory without any applications running.











Comments