One of the strong management points of Windows 7 deployment is the ability to manage you images without having to apply the image, make the changes, and then recapture the image. DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) allows you to mount a Windows image and make configuration changes to it. All this while not having to take the time to first deploy the image.
To begin working with an image, we need to mount it. First, make a new folder to hold the mounted image. For this demo, I made one called ImageMount. Both the folder and the image file are on my D: drive.
Next, open a command prompt with elevated permissions.
The .wim file I’m using for this demo is the install.wim file from the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation media.
Browse to the location where you stored the image file and the folder to mount it in.
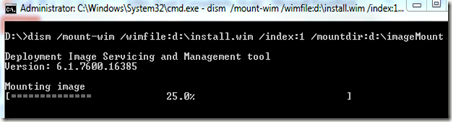
Type DISM /mount-wim /wimfile:d:\install.wim /index:1 /Mountdir:d:\ImageMount
Depending on the size of the WIM file, this may take a few minutes,
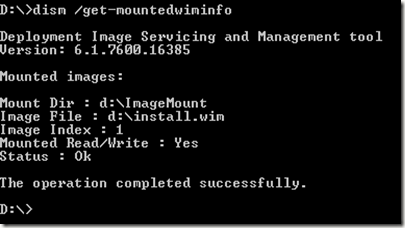
Once completed, you can get information on the mounted WIM file by typing: DISM /get-mountedwiminfo and pressing Enter.
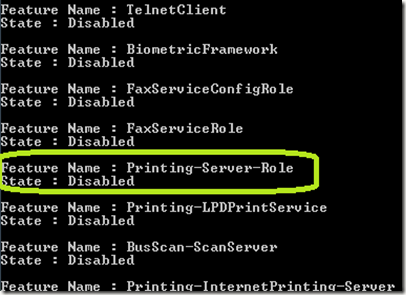
Here we are going to take a look at enabling and disabling features in a Windows 7 image. To get a list of the features, type DISM /image:d:\ImageMount /get-features and press Enter. Below is just a small sampling of what was returned.
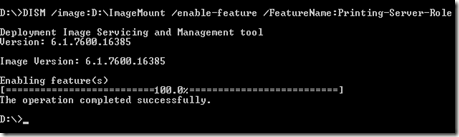
We are going to enable the Printing-Server-Role
Type DISM /image:D:\ImageMount /enable-feature /FeatureName:Printing-Server-Role and press Enter.
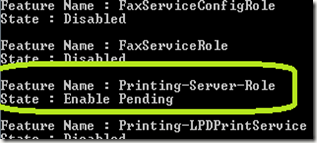
You should see the message above if all went well. By once again typing DISM /image:d:\ImageMount /get-features and pressing Enter, you should see the feature has been “Enable Pending.” This indicates the Optional Component is installed and enabled.
You can disable a feature by typing DISM /image:D:\ImageMount /Remove-feature /FeatureName:Printing-Server-Role and pressing Enter.
To commit the changes and close the image for use, type DISM /Unmount-Wim /MountDir:D:\ImageMount /Commit. If you do not want to save your changes, replace /Commit to /Discard.
To begin working with an image, we need to mount it. First, make a new folder to hold the mounted image. For this demo, I made one called ImageMount. Both the folder and the image file are on my D: drive.
Next, open a command prompt with elevated permissions.
The .wim file I’m using for this demo is the install.wim file from the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation media.
Browse to the location where you stored the image file and the folder to mount it in.
Type DISM /mount-wim /wimfile:d:\install.wim /index:1 /Mountdir:d:\ImageMount
Depending on the size of the WIM file, this may take a few minutes,

Once completed, you can get information on the mounted WIM file by typing: DISM /get-mountedwiminfo and pressing Enter.

Here we are going to take a look at enabling and disabling features in a Windows 7 image. To get a list of the features, type DISM /image:d:\ImageMount /get-features and press Enter. Below is just a small sampling of what was returned.

We are going to enable the Printing-Server-Role
Type DISM /image:D:\ImageMount /enable-feature /FeatureName:Printing-Server-Role and press Enter.

You should see the message above if all went well. By once again typing DISM /image:d:\ImageMount /get-features and pressing Enter, you should see the feature has been “Enable Pending.” This indicates the Optional Component is installed and enabled.

You can disable a feature by typing DISM /image:D:\ImageMount /Remove-feature /FeatureName:Printing-Server-Role and pressing Enter.
To commit the changes and close the image for use, type DISM /Unmount-Wim /MountDir:D:\ImageMount /Commit. If you do not want to save your changes, replace /Commit to /Discard.
Comments