System Center Virtual Machine Manager uses metrics on each managed host to determine if the host is suitable for the placement of a new VM. The metrics that are evaluated are:
You can configure VMM to place a higher or lower weight on each of these metrics to better fit your needs. For example, if you are placing a high degree of emphasis on CPU utilization and you are deploying a VM that will require 4 CPUs, then only hosts with low CPU utilization will be selected for placement of that VM. Here is how you can customized the metrics.
Open SCVMM.
In the left pane at the bottom, click Administration
In the General pane, click Placement Settings.
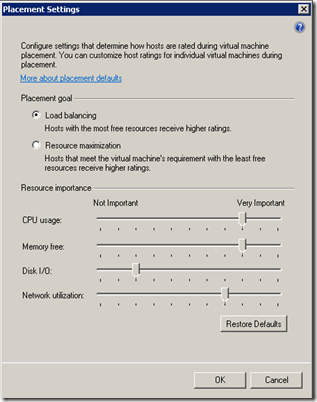
The first two radio buttons allow you to balance the VM load or to maximize the servers resource utilization.
The slider bars tell SCVMM what metrics are the most important to you.
- CPU Usage
- Memory Free
- Disk I/O
- Network Utilization
You can configure VMM to place a higher or lower weight on each of these metrics to better fit your needs. For example, if you are placing a high degree of emphasis on CPU utilization and you are deploying a VM that will require 4 CPUs, then only hosts with low CPU utilization will be selected for placement of that VM. Here is how you can customized the metrics.
Open SCVMM.
In the left pane at the bottom, click Administration
In the General pane, click Placement Settings.

The first two radio buttons allow you to balance the VM load or to maximize the servers resource utilization.
The slider bars tell SCVMM what metrics are the most important to you.
Comments