System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) allows you to manage multiple virtualization hosts from one console. With other virtual management software, you can only manage the virtual machines (VMs) on the local host. With SCVMM, you can manage the VMs on hosts running Hyper-V, Virtual Server 2005 R2, and VMWare ESX Server.
First off, you need a copy of SCVMM. You can download a 180 day trial version here.
Once you download a copy, you simple need to install it. First, execute the installation file with administrative level permissions.
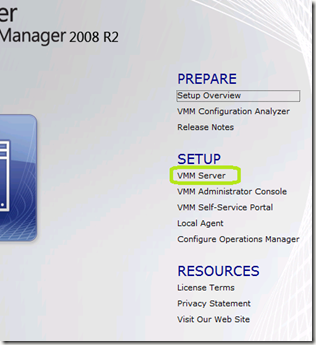
Click VMM Server
Select I accept the terms of this agreement and click Next
On the Microsoft Update window, click what is appropriate for your environment and then click Next.
On the Customer Experience Improvement Program window, click what is appropriate for you and then click Next.
On the Product Registration page, enter your name and organization. Click Next.
The Prerequisites Check page will automatically check for required components. Fix any errors it detects.
Click Next to continue.
On the Installation Location page, set the installation path and click Next.
On the SQL Server Settings page, choose the SQL installation that is appropriate for you. Provide any required information for your organizations SQL setup. Click Next.
On the Library Share Settings page, accept the defaults and click Next.
On the Installation Settings page, accept the defaults and click Next.
On the Summary of Settings page, click Install.
It is recommended that you leave Check for the latest Virtual Machine Manager updates checked.
Click Close.
That’s all it takes.
First off, you need a copy of SCVMM. You can download a 180 day trial version here.
Once you download a copy, you simple need to install it. First, execute the installation file with administrative level permissions.
Click VMM Server

Select I accept the terms of this agreement and click Next
On the Microsoft Update window, click what is appropriate for your environment and then click Next.
On the Customer Experience Improvement Program window, click what is appropriate for you and then click Next.
On the Product Registration page, enter your name and organization. Click Next.
The Prerequisites Check page will automatically check for required components. Fix any errors it detects.
Click Next to continue.
On the Installation Location page, set the installation path and click Next.
On the SQL Server Settings page, choose the SQL installation that is appropriate for you. Provide any required information for your organizations SQL setup. Click Next.
On the Library Share Settings page, accept the defaults and click Next.
On the Installation Settings page, accept the defaults and click Next.
On the Summary of Settings page, click Install.
It is recommended that you leave Check for the latest Virtual Machine Manager updates checked.
Click Close.
That’s all it takes.
Comments