In small environments, one individual may be charged with managing your Hyper-V environment. In larger organizations, the tasks of maintaining Hyper-V may need to be distributed. In order to stick to the Principal of Least Privilege, you have the ability to delegate out the management tasks of Hyper-V to multiple users.
To do this log into your 2008 server that is hosting Hyper-V.
· Click Start, type MMC and press Enter
· Click File and then click Add/Remove Snap-in…
· In the Available snap-ins: list, click Authorization Manager.
· Click Add and then OK.
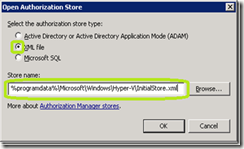
· In the MMC console, right click Authorization Manager and select Open Authorization Store…
· Verify that XML file is select and type %programdata%\Microsoft\Windows\Hyper-V\InitialStore.xml in the Store name:
· Click OK
From here we can define scopes to limit the Hyper-V servers that users can manage. We can also define roles that users can participate in and what those roles can do. Below is a list of the possible delegations and a short description of each:
- Allow Input to Virtual Machine
- Allow Output from Virtual Machine
- Allow Virtual Machine Snapshot
- Bind External Ethernet Port
- Change Virtual Machine Authorization Scope
- Change VLAN Configuration on Port
- Connect Virtual Switch Port
- Connect Internal Ethernet Port
- Create Virtual Machine
- Create Virtual Switch
- Create Virtual Switch Port
- Delete Internal Ethernet Port
- Delete Virtual Machine
- Delete Virtual Switch
- Delete Virtual Switch Port
- Disconnect Virtual Switch Port
- Modify Internal Ethernet Port
- Modify Switch Port Settings
- Modify Switch Settings
- Pause and Restart Virtual Machine
- Read Service Configuration
- Reconfigure Service
- Reconfigure Virtual Machine
- Start Virtual Machine
- Stop Virtual Machine
- Unbind External Ethernet Ports
- View External Ethernet Ports
- View Internal Ethernet Ports
- View LAN Endpoints
- View Switch Ports
- View Switches
- View Virtual Machine Configuration
- View Virtual Switch Management Service
- View VLAN Settings
Creating a Scope
· Expand Authorization Manager \ InitialStore.xml.
· Right click Hyper-V Services and then click New Scope…
· In the New Scope window, provide a name and a description of up to 1024 characters for this scope.
· Click OK.
I called this scope, View Hyper-V Configurations.
We now need to define the different Role Definitions and Task Definitions. Both definitions allow you to determine what a user, or a group of users are able to do. With Role Definitions, you can use inheritance just like in NTFS permissions. Another difference is that you can assign both a task, and an operation to a Role Definition. In a Task Definition, you can only assign a operation.
To create a new Role to Task Definition, expand the scope you just created.
· Expand Definitions.
· Right click either Role Definition or Task Definition and select New.
· Expand Authorization Manager \ Hyper-V Services \ Definitions
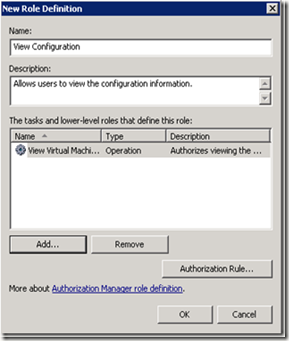
· Right click Role Definitions and select New Role Definition.
· Click Add…
· Click the Operations tab.
· Provide a name and a description for this Role.
· Click Add…
You can add the Role Definitions you have already created and inherited those rules into this definition.
In our case, no roles other than administrator have been created. Do not check Administrator. This will allow the users to do everything.
· Click the Tasks tab.
· If you have created any tasks, they will be available to add to this role. Otherwise just click OK and at the warning.
· Click the Operations tab.
· Select the operations that you would like the users to perform and then click OK.
· Click OK once again.
We now need to assign the role to the scope and add users and groups into the role.
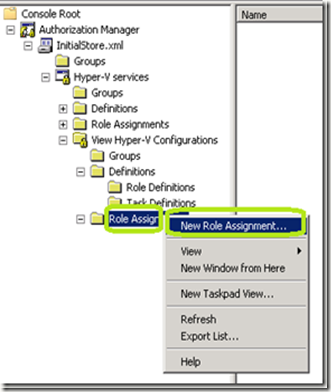
· Expand the Role Definition that you created and then right click Role Assignments
· Click New Role Assignment…
· Check the box of the Role Definitions that you want to assign to this definition.
· Click OK
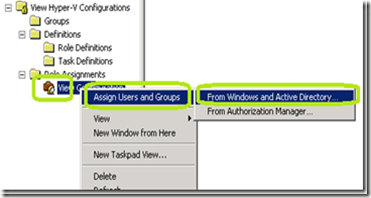
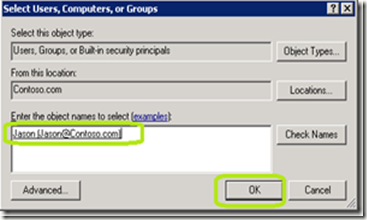
· Right click the assigned definition and click Assign Users and Groups and then From Windows and Active Directory
· Add in Users and groups and then Click OK
Those users and groups are now authorized to perform the delegated tasks on that host.


Comments