System Center Virtual Machine Manager allows you to install the Hyper-V role on Server 2008 R2 from the VMM console. To do this, the target machine must be part of the domain the VMM server is a member of.
Open System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
In the lower left, click Hosts.

Click All Hosts in the upper left, and then click Add Host in the Actions pane.
Select Windows Server-based host on an Active Directory domain/
Provide a User name, Password, and Domain names.
Click Next.

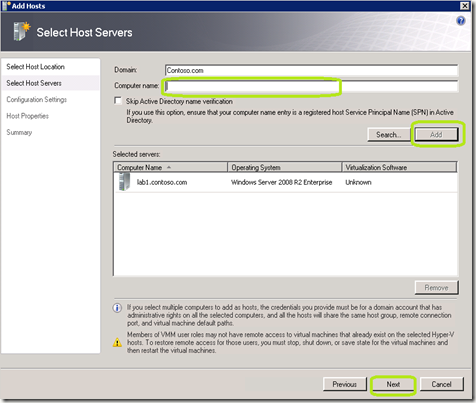
In the Computer Name field, type the name of the server.
Click Add.
Click Next.
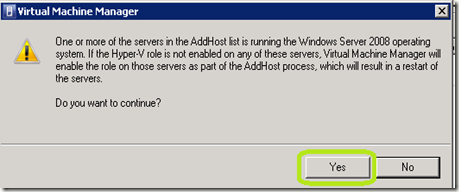
Next you will receive a Virtutal Machine Manager warning letting you know that if this host is a 2008 server that does not have Hyper-V installed, it will reboot the server. Click Yes.
In the Configuration Settings window, select the host group that you to join this host to and then click Next.
Note: In the event that this host is being managed by another VMM server, you can click Reassociate host with this Virtual Machine Manager server before clicking Next. This will transfer management of the target server to the VMM server you are currently using.
On the Host Properties window, you can set the default location for virtual machines for this host. You can perform this step later if you wish. Click Next.
Click Add Hosts.
The installation will take a few minutes to complete. You will see the job screen below to help you monitor the installation progress. It will take several minutes before the first progress bar starts to move.

No warnings will be given in this console, or on the target server before the reboot takes place. In practice, two back to back reboots will take place. You will not have an opportunity to interact with the target server between the two reboots.
A minute or two after the target server comes online, the job on the VMM server will be completed.
The PowerShell code for this procedure looks like this:
$Credential = get-credential
$VMHostGroup = Get-VMHostGroup -VMMServer localhost | where {$_.Path -eq "All Hosts\Test Lab Servers"}
Add-VMHost -VMMServer localhost -ComputerName "lab1.contoso.com" -Description "" -Credential $Credential -RemoteConnectEnabled $true -VmPaths "" -Reassociate $false -RunAsynchronously -VMHostGroup $VMHostGroup
Open System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
In the lower left, click Hosts.

Click All Hosts in the upper left, and then click Add Host in the Actions pane.
Select Windows Server-based host on an Active Directory domain/
Provide a User name, Password, and Domain names.
Click Next.

In the Computer Name field, type the name of the server.
Click Add.
Click Next.

Next you will receive a Virtutal Machine Manager warning letting you know that if this host is a 2008 server that does not have Hyper-V installed, it will reboot the server. Click Yes.

In the Configuration Settings window, select the host group that you to join this host to and then click Next.
Note: In the event that this host is being managed by another VMM server, you can click Reassociate host with this Virtual Machine Manager server before clicking Next. This will transfer management of the target server to the VMM server you are currently using.
On the Host Properties window, you can set the default location for virtual machines for this host. You can perform this step later if you wish. Click Next.
Click Add Hosts.
The installation will take a few minutes to complete. You will see the job screen below to help you monitor the installation progress. It will take several minutes before the first progress bar starts to move.

No warnings will be given in this console, or on the target server before the reboot takes place. In practice, two back to back reboots will take place. You will not have an opportunity to interact with the target server between the two reboots.
A minute or two after the target server comes online, the job on the VMM server will be completed.
The PowerShell code for this procedure looks like this:
$Credential = get-credential
$VMHostGroup = Get-VMHostGroup -VMMServer localhost | where {$_.Path -eq "All Hosts\Test Lab Servers"}
Add-VMHost -VMMServer localhost -ComputerName "lab1.contoso.com" -Description "" -Credential $Credential -RemoteConnectEnabled $true -VmPaths "" -Reassociate $false -RunAsynchronously -VMHostGroup $VMHostGroup
Comments