Backing up your EFS key can help you recover files in the event you suffer a hard drive loss. Obviously this will not help recover lost file on the crashed hard drive. For those encrypted files on the crashed hard drive, hopefully you have good backups. To back up the EFS certificate on your client, you first need to make sure you have encrypted at least one file or folder.
Open a command prompt and type Cipher /y
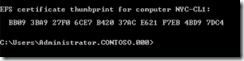
This displays your EFS certificate thumbprint. Now that we have established that you have one, lets back it up. Type Cipher /x.
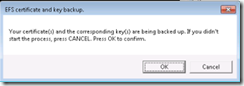
Click OK.
Provide a name for the file you want to export to certificate to.
Provide a password and confirm it to protect the key.
To recover the certificate, you need to use the certificate mmc.
-
The end user who owns the certificate must log on to the destination computer.
-
Open MMC by typing mmc in the Run dialog box.
-
In the File menu, click Add/Remove Snap-in.
-
In the Add/Remove Snap-in dialog box, click Add.
-
Select Certificates from the list, click Add, and then select My user account.
-
Click Finish, click Close, and then click OK.
-
Browse to Certificates - Current user\Personal.
-
Right-click Personal.
-
Click All Tasks, and then click Import.
-
Use the Certificate Import Wizard to locate the certificate that you exported. When browsing for the certificate, you should select Personal Information Exchange (*.pfx; *.p12) from the Files of type dropdown list box. You will need to enter the password you supplied when you exported the certificate from the destination computer.
-
Upon completion, you will receive a message that the import was successful.
Comments