Windows already protects your account passwords by first storing only a hash of the password, and then encrypting that hash. You an increase protection of the database by either removing the SAM database encryption key to removable media, or by requiring a start-up password to unlock the database. A word of caution, you will need a trusted administrator at the console of the server when you restart it to insert the media or type the password. This document looks at setting up a password to unlock the SAM Database
On you Windows Server or client, click Start.
Type SYSkey and press Enter
If User Access Control (UAC) is enabled, you may need to provide the proper credentials.
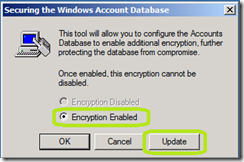
Encryption Enabled should already be selected for you. Click Update.
Select Password Startup.
Provide and confirm the password you want to lose.
Warning: If you lose this password, you lose access to this computer.
Click OK.
Click OK at the confirmation screen.
Now, reboot the server/client.
The computer will go through the normal boot process, but it will stop at the screen below.
Type in the Password you choose and click OK.
At this point, the system will complete the boot.
To remove this password from the startup, you will need to return the key to the local system
Click Start, type SYSkey and press Enter.
If User Access Control (UAC) is enabled, you may need to provide the proper credentials.
Encryption Enabled should already be selected for you. Click Update.
Select System Generated Password.
Verify that Store Startup Key Locally is selected
Click OK.
Type in the password you used to unlock the database and click OK.
Click OK at the confirmation screen.
A restart of the machine will let it boot normally.






Comments