Last week I published an article about how to set your host reserves in VMM Manager. I deliberately left off with a manual task. Changing the host reserves only affects new hosts added to your VMM environment. What about the ones that are already there? You had to manually change them.
Using PowerShell on a client that has VMM Manager installed on it, you can change the Host Reserves of all Hosts that are already on the system
Open PowerShell (You must do this on a client that has VMM Manager installed on it)
Type Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager and press Enter.
This adds in cmdlets that are specific to Virtual Machine Manager.
Now type Get-VMHost | Select-Object ComputerName, CPUPercentageReserve, NetworkPercentageReserve, DiskSpaceReserveMB, MaxDiskIOReservation, MemoryReservationMB and press Enter.
This will show you the current Host Reserves on each host.
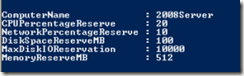
We can use the 5 reservation properties to change the host reservations. For simplicity, we are only going to change the CPU and Network percentage reserves.
Get-VMHost | Set-VMHost –CPUPercentageReserve 25 –NetworkPercentageReserve 35
If we re-execute our first command, we get the following:

Using PowerShell on a client that has VMM Manager installed on it, you can change the Host Reserves of all Hosts that are already on the system
Open PowerShell (You must do this on a client that has VMM Manager installed on it)
Type Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager and press Enter.
This adds in cmdlets that are specific to Virtual Machine Manager.
Now type Get-VMHost | Select-Object ComputerName, CPUPercentageReserve, NetworkPercentageReserve, DiskSpaceReserveMB, MaxDiskIOReservation, MemoryReservationMB and press Enter.
This will show you the current Host Reserves on each host.

We can use the 5 reservation properties to change the host reservations. For simplicity, we are only going to change the CPU and Network percentage reserves.
Get-VMHost | Set-VMHost –CPUPercentageReserve 25 –NetworkPercentageReserve 35
If we re-execute our first command, we get the following:

Comments