With Sever 2012, you can still use the old Disk Management MMC to manage disks like you have since Windows 2000. In Server 2012, you have a new option. For Server 2012 you can use the File and Storage Services in Server Manager to accomplish the tasks that you use to perform in the Disk Manager.
Open Server Manager and click File and Storage Services.
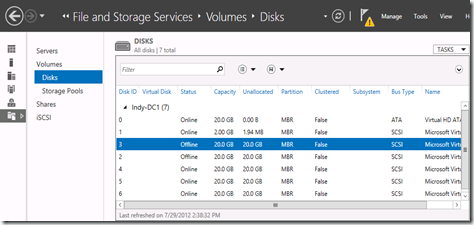
Click on the Disks menu item. Take a look below.
You can see that Disk 0 is offline.
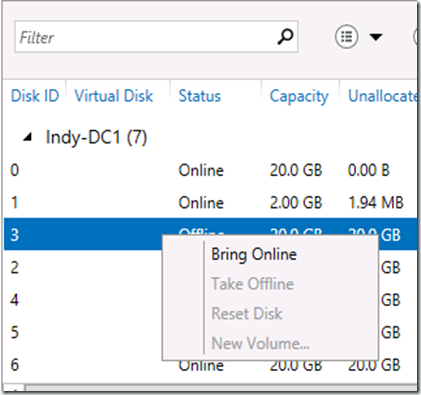
Right click disk 3 and select Bring Online.
Click Yes to confirm if prompted.
To format the disk, right click it again and select New Volume.
Click Next.
If you are managing the disks on a different server, make sure you select the correct server. Also, click the disk the create the volume on.
Click Next.
Select how much of the drive that you want to include in the volume and click Next. The default is the maximum drive capacity.
On the Assign to a drive letter or folder window, select what is appropriate for your environment.
Click Next.
The two available file systems are NTFS and ReFS.
Provide a volume label.
Take note of the option to force this drive to only use 8 character names. This is to help with backward compatibility with older 16 bit applications and is not recommended.
Click Next.
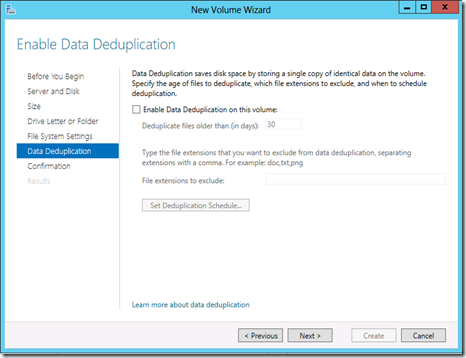
The Enable Data Deduplication window will be new to most users. Data deduplication helps to save considerably on areas where static data is stored. You can enable data deuplication on this volume now if you wish. Click Learn more about data deduplication before enabling this option.
Click Next.
Click Create.
Click Close.
Click on the disk ID in File and Storage Services window in Server Manager that you just worked on to see your new volume.
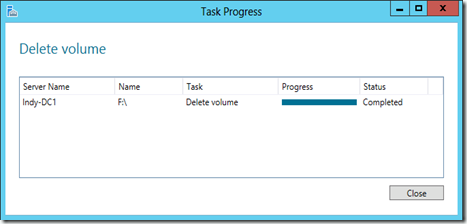
If you need to delete the volume, right click it and select Delete Volume.
Click Yes at the confirmation.
Click Close when the wizard completes.




Comments