Over many years as a Network Administrator, I constantly struggled with the data storage needs of my users. Not only did we need to allocate funds for greater amounts of storage, but also greater amounts of funds for backup and recovery operations that would meet the needs of the organization.
One of the big problems was duplicate information being stored by multiple users. Duplicate data adds to your cost in several ways.
· Increase in storage cost due to capacity depletion from duplicated data.
· Increased number of backup media, and the cost associated with storage, transportation, and replacement of the media.
· Increased recovery times.
· Purchasing and deployment of new disaster recovery hardware so backup and recovery operations can stay within established time frames.
Data Deduplication can help reduce the cost of the above bulleted points. Data deduplication will remove duplicated blocks of data and place references to a single copy stored on the volume. It works well for data stores that are not frequently changed and will not work on boot partitions or partitions containing the operating system. You can achieve reduced storage capacity for file shares, software deployment shares, and virtual hard disk libraries. Data deduplication is only support on the NTFS file system and not on the new Resilient File System (ReFS).
Here is how you turn it on.
First we need some duplicate files. (OK, not really, but I wanted to have some files on the drive.)
Here you can see that we have a couple of files that are store in different locations, but are duplicates of each other. They also reside on an NTFS formatted volume that does not contain the boot or OS partition.
Open Server Manager and click Manager –> Add Roles and Features.
Click Next three times.
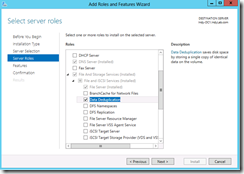
Expand File and Storage Services –> File and iSCSI Services.
Check Data Deduplication and click Next.
Click Next and then Install.
Click Close.
You can monitor the installation in Server Manager.
No restart is necessary.
On the Server Manager click File and Storage Services.
Click Volumes
Right click the E: drive and select Configure Data Deduplication. (Note: it may take a few minutes before you can select Configure Data Deduplication.)
Check Enable data deduplication.
Click Set Deduplication Schedule
Check Enable throughput optimization. This will set the time when data deduplication will run with normal priority. This allows time for more processor capacity to be dedicated to the deduplication process.
Click OK twice.
Data Deduplication is now set up.




Comments