Microsoft’s Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT) Allows you to collect hardware and software inventory information in your domain to help assist you in preparing for client upgrades. The idea is for you to be able to collect the types of software that are running on your clients so you can test and mitigate any compatibility issues before deploying the images of Windows 7. This is a very nice, useful, and free application
In using the ACT, I needed to manually install the Data Collection Package on each client using administrative permissions. For a small organization, this may be acceptable. In larger organizations, you may need a more automated deployment method.
An easy way to deploy these packages to your clients is through Group Policy. Before we begin, I need to point out a drawback of a GPO software deployment. You have no idea if it worked or not. System Center Operations Manager allows you to do software deployments and provide reports so you know if all went well. Of course, this comes at a price. When doing application compatibility testing, you only need a sampling of the clients and applications in your environment. The important thing is to just make sure you have a sampling of every application.
For this demonstration, I created an Organizational Unit in Active Directory called Clients. I placed a Windows Vista and Windows 7 client in this OU. I also created a data collection set in ACT 5.6 called MCTExpert_Data_Collection_PKG and placed it in a shared folder called Data.
Next I open Group Policy Management Console on my domain controller.
Expand Forest \ Domain Name \ Group Policy Objects.
Right click Group Policy Objects and click New
Provide a name for this GPO. I called this one ACT_Data_Collection Click OK.
Right click ACT_Data_Collection and select Edit.
To ensure that this package is installed without a UAC prompt, we are going to assign it to the Computer Configuration. Expand Computer Configuration \ Policies \ Software Settings.
Right click Software Installation and click New \ Package.
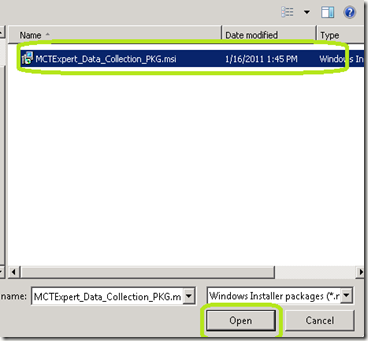
Browse to the shared folder and select your package. Make sure you browse by UNC path. Click Open.
On the Deploy Software page select Assigned and then click OK.
Close the Group Policy Management Editor window.
In the Group Policy Management window, link the policy ACT_Data_Collection to the GPO containing the clients that you want to collect data on. Click OK
You will need to reboot your clients for this to take effect.
A quick check after the reboot using GPResult /r shows that the policy did apply. Remember that 2 reboots may be necessary before you begin to receive reports.
In the Application Compatibility Manager, refresh your reports and you will being to see the reports on your clients begin to populate.

In using the ACT, I needed to manually install the Data Collection Package on each client using administrative permissions. For a small organization, this may be acceptable. In larger organizations, you may need a more automated deployment method.
An easy way to deploy these packages to your clients is through Group Policy. Before we begin, I need to point out a drawback of a GPO software deployment. You have no idea if it worked or not. System Center Operations Manager allows you to do software deployments and provide reports so you know if all went well. Of course, this comes at a price. When doing application compatibility testing, you only need a sampling of the clients and applications in your environment. The important thing is to just make sure you have a sampling of every application.
For this demonstration, I created an Organizational Unit in Active Directory called Clients. I placed a Windows Vista and Windows 7 client in this OU. I also created a data collection set in ACT 5.6 called MCTExpert_Data_Collection_PKG and placed it in a shared folder called Data.
Next I open Group Policy Management Console on my domain controller.
Expand Forest \ Domain Name \ Group Policy Objects.
Right click Group Policy Objects and click New
Provide a name for this GPO. I called this one ACT_Data_Collection Click OK.
Right click ACT_Data_Collection and select Edit.
To ensure that this package is installed without a UAC prompt, we are going to assign it to the Computer Configuration. Expand Computer Configuration \ Policies \ Software Settings.
Right click Software Installation and click New \ Package.
Browse to the shared folder and select your package. Make sure you browse by UNC path. Click Open.

On the Deploy Software page select Assigned and then click OK.
Close the Group Policy Management Editor window.
In the Group Policy Management window, link the policy ACT_Data_Collection to the GPO containing the clients that you want to collect data on. Click OK
You will need to reboot your clients for this to take effect.
A quick check after the reboot using GPResult /r shows that the policy did apply. Remember that 2 reboots may be necessary before you begin to receive reports.
In the Application Compatibility Manager, refresh your reports and you will being to see the reports on your clients begin to populate.

Comments