By and far, one of my favorite features of Windows 7 was the search feature. I am not a fan of the control panel and the search feature kept me from going in there. With the new Windows 8 interface, called “Metro”, it may be a bit hard at first to find the search feature.
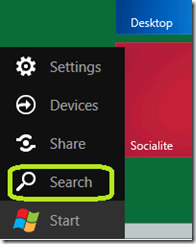
To open Search. take your pointing device to the lower left hand corner and move it into the grey area pointed out below. Once there, move it to the lower right hand corner.
Click Search from the menu that appears.
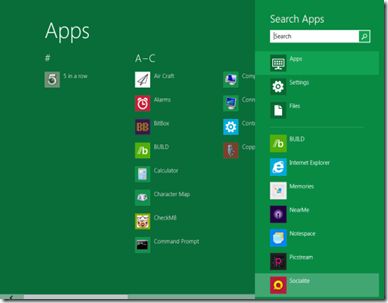
The new search feature appears.
You can click on one of the icons under search to go to that site or browse the list of applications behind the Search window. You can also type your query in the Search field.
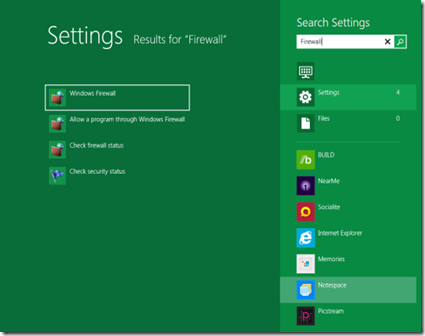
In the below example, I typed in Firewall. This is how I would normally get to the Windows Advanced Firewall. Notice how the results are displayed/
Under Settings there are now 4 objects listed. Once I clicked on Settings, the objects the search found are listed to the left and I can click (or tap) on the one that I want to open.


Comments