BitLocker allows you to achieve total hard drive encryption. Windows has had EFS capability since Windows 2000. EFS allowed you to encrypt individual folders and files. BitLocker allows for an entire drive to be protected. Not all versions of Windows 7 support BitLocker. You need to have either the Enterprise or Ultimate editions to encrypt removable media. Windows Vista also had BitLocker, but it could only encrypt the boot partition of a client. The new version that shipped with Windows 7, called BitLocker-to-go, can encrypted removable drives as well.
What if you need to use a BitLocker encrypted drive on a version of Windows 7 that does not support BitLocker encryption? No problem. The screen shots below are going to be from a Windows Home Premium edition. When I insert my USB hard drive that is BitLocker encrypted, I see this icon in Windows Explorer.
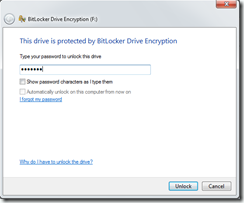
You can either right mouse click the drive and select Unlock Drive… or just wait for the auto play to start as below. Type in the password that you used to encrypt the drive.
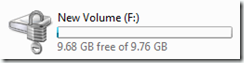
Once the password is accepted, your drive is unlocked.
We can see that Authenticated Users on this client have been given the security right to both read and write to this drive.

Comments